If you’ve done any level of content SEO, you’ll know that you can publish a Shakespeare level masterpiece, but if it sits on a low authority domain, no clicks, no social signals, no internals, and worse of all, NO BACKLINKS?! It’ll be a ghost town…
Meanwhile, thin, mediocre content on a DR90 news site will outrank you all day. Why? Because Google still leans on links as its #1 external signal for everything from authority, to consensus building (from the linkgraph), to trust, to anti-spam, to validation, to raw power.
-
Content without backlinks = invisible.
-
Backlinks without content = short term play, unless you’re an authority site.
-
Backlinks + content + authority stacking = Money Printer!
That’s why the smartest SEOs obsess over link velocity, anchor distribution, and entity stacking instead of praying to the Google documentation gods that they don’t get slapped by another classifier.
In this guide, I’ll break down why backlinks matter, what separates garbage links from power links, and the systems you need if you actually want to compete in 2026’s highly volatile SEO arena.
Forget the white hat glazing about building good content and waiting an eternity for natural links to magically take you to position one. This is the real playbook.
Why Backlinks Are Still #1 in SEO
When I first started my career, spam ruled the roost. Automated link building to manipulate PageRank meant you could rank for keywords with crazy ROI, and especially in niches where the other competitors weren’t utilizing spam.
Since then, Google has rolled out update after update for 20+ years trying to “kill” inorganic link building. Penguin, spam classifiers, link scheme guidelines, disavows, manual actions, they’ve released a whole arsenal!
They did make some genuine progress with a lot of those updates, but over the last 12-36 months, there is a growing amount of evidence for serious regression in the algorithm…
-
Content signals? AI spam nuked that. Anyone with ChatGPT can churn out 100 mediocre niche blog posts overnight, fully equipped with realistic images and even now video.
-
User signals? CTR manipulation, bot traffic, behavioral spoofing, all hackable and currently being actively targeted by Google.
-
OnPage optimization? Baseline requirement, not a differentiator, especially in competitive niches.
But backlinks? They’re the one signal Google can’t fully neutralize because they underpin how the web itself works. The linkgraph is literally Google’s operating system.
And even the most hard core of white hats will agree that fundamentally, links improve crawling and help validate you on the knowledge graph which will boost your brands trust signals.
So at the minimum, you should be building out your entity stacking, you can watch my video on that here –
And at the maximum, you should be trying to get every link that you can find that intersects with your top 10-50 biggest niche & SERP competitors – As well as boosting any page that independently needs links to either rank itself or pass juice to a page that needs it to.
Not All Links Are Created Equal
If backlinks are search engine currency, then most of the coins are counterfeits that won’t get you very far…
You could stack thousands of junk links from random directories, web 2.0s, automated blog comments, and Fiverr PBNs, but if they’re not contextual, relevant, and from trusted, relevant or authoritative sources, they’re more likely to do damage than good.
Google doesn’t treat all links the same because:
-
Authority Differential:
A DR90 editorial mention from Forbes on a highly relevant page with low OBL will hit harder than 10,000 directory links. Why? Because high authority sites are reference hubs in Google’s eyes. -
Relevance Matters:
A link with decent traffic and RD from a top tier casino news site that links to all of your biggest competitors? Powerful. The same link from a lifestyle blog about vegan cupcakes? Weak. Context transfers strength. -
Placement Power:
Links buried in a footer or sidebar scream paid/unnatural. Contextual, inbody editorial links, especially surrounded by semantically related terms, pack more juice. -
Traffic + Indexation:
A backlink on a page that nobody visits and Google barely crawls is worthless. A link sitting on a live, indexed, high-traffic news piece? Now we’re talking. -
Toxic Profiles:
Link farms, hacked domains, and spam networks are like steroids — short-term gains, long-term collapse. Google’s August and September updates hammered orphaned parasite pages and garbage tier sites.
Most of the link inventory out there is the same lists repeatedly amongst every vendor and has just become neutralized noise. That’s why operators who understand quality control dominate, they’re filtering the trash and securing links that actually move the needle.
In almost every client audit I’ve done, sites with fewer, stronger links consistently outperformed bloated backlink profiles stuffed with weak junk. The game is ROI, not raw numbers.
So when people whine “but I built 500 links and my rankings didn’t move,” the answer is simple: You bought or built garbage with zero due diligence, and likely from the completely wrong buyer.
What Are Spam Links?
Spam links are the annoying noise of the web…
Think:
- Automated domain lists and SEO spam.
-
Blog comment blasts.
-
Mass directory submissions.
-
Web 2.0s with spun content.
-
Auto-generated sidebar and footer links.
Example of telegram spam links in Ahrefs pointed to our site:
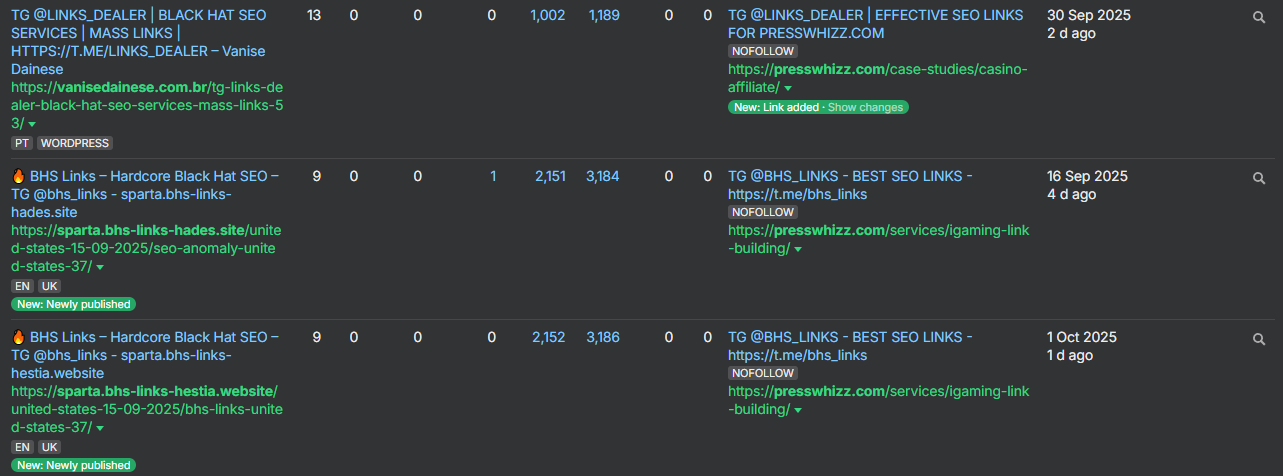
They’re VERY cheap, fast, and everywhere… And there are a variety of different reasons to use them.
What Are Toxic Links?
Toxic links are a different beast though. Google has slowly made a lot less links “toxic” (aka, it will pass on a negative signal to the page its linking to) to just neutralizing links (sending no/neutral signal) instead, likely in a cost saving effort.
But they do still exist…
These are links that don’t just get ignored, they actively drag your site down. They come from:
-
Link farms & PBN networks burned into the ground.
-
Hacked domains spreading bad niche neighborhood links everywhere.
-
301 spam chains where penalized sites get redirected into yours.
-
Foreign language adult/casino/pharma mashups that have nothing to do with your site.
Unlike spam, toxic links can trigger manual actions or algorithmic suppression, though 99.9% of SEOs aren’t capable of doing negative SEO with them.
Google doesn’t do this often anymore (cost saving, as mentioned earlier), but when they do, it is brutal.
Signs of toxicity:
-
Sudden flood of links from deindexed or malware-ridden domains.
-
Unnatural anchor text blasts (exact-match spam anchors pointing at one page).
-
Sitewide links from irrelevant, low-quality networks.
Toxic links are the SEO equivalent of steroids gone wrong: short-term bulk, long-term organ failure.
If spam links are static, toxic links are radioactive. Manage them, disavow them if necessary, and most importantly, don’t be the muppet buying them from a $20 “10,000 backlinks guaranteed” gig.
What To Look For in Quality Backlinks
Now we know what NOT to build, I’ll give you a small guide on what to look for, and how to do due diligence on, quality links that you can build for your campaign.
The problem is, most SEOs think “quality” means “high DR” or some other meaningless vanity metric, and stop there…
A true quality backlink is a cocktail of multiple factors working together. Get them right, and you’ll see rankings move in weeks. Miss them, and you’ll blow budget on links that don’t move the needle.
Here’s my 7 step link checklist:
1. Authority That Transfers Power
-
Domain Metrics: Yes, DR/DA is a quick litmus test. But DR80 sites can be spam graveyards and a traffic graph that died a long time ago… Look deeper.
-
Traffic Reality Check: Always cross reference with organic traffic estimates. A DR80 with <500 monthly visits? Likely a dead or manipulated domain, or targets traffic outside of search engines.
-
Authority Flow, Not Vanity: You want authority flowing from page → to your link, not just sitting at the root domain with no internal signals, and a category that specifically stops it from showing on the homepage… Look for indexed pages with their own links & signals, not orphaned ghost articles.
Pro Tip: Filter for pages that have your keyword or niche/topic on it, even if the site isn’t ranking, pre-coverage of a topic can mean significantly stronger link signals.
2. Relevance Is Non-Negotiable
-
Topical Fit: Build in your niche and associated niches, with authority publications have niche pages linking. As an example, think fintech SaaS getting links from a finance news site, a B2B SaaS blog, or even a legal compliance hub.
-
SERP Relevance: Check whether the linking site itself ranks for related keywords. If it doesn’t, it’s not a trusted topical authority.
-
Category Context: Avoid sites with “kitchen sink” content: Casino + crypto + CBD + pet food on the same blogroll? Probably a bit too broad for my liking…
Pro Tip: Think like Google’s Knowledge Graph, every link should reinforce your entity inside a relevant cluster, and association is very linear between categories/topics.
3. Placement = Gold or Garbage
-
Contextual Body Links: Editorial, in content, surrounded by semantically relevant words.
-
Avoid Sitewide: Footer, sidebar, blogroll are good for users, most search engines just ignore them, especially if they are using menu microdata.
-
Position on Page: Links higher up in the content (above the fold) tend to pass more weight than buried in a 2,000 word rant, but we still prefer matching context over position.
-
Outbound Link Ratio (OBL): If the page is linking out to 70+ random sites on a 900 word blog post, your link is diluted to dust.
Pro Tip: Don’t bake in authority sources for the sake of it, focus guest posts on tailoring the content, context, anchor and equity it moves. Each link built, especially over a certain price point, should be treated as an asset.
4. Traffic + Indexation = Proof of Life
-
Live Traffic: Backlinks on zombie pages (indexed but with zero impressions/clicks) generally take longer to get crawled and have a smaller impact. This is why we recommend (and when we do our managed link building service) building optimized content and ranking your guest posts.
-
Indexation Test: Search the exact page in Google (
site:domain.com "title of article"). If it doesn’t show up? Google’s ignoring it. Use trackers to make sure publishers don’t delete the page or switch the tag to nofollow later on. -
Referral Traffic Potential: High quality links should also drive real humans. Even 10-50 monthly visitors from the right audience is worth gold…
Pro Tip: This is less of a tip, but always remember, backlinks without indexation = setting your cash and time on fire!
5. Clean History & Link Profile
-
Check Historical Anchors: Did the domain used to rank for pharma/pills/porn before its “rebrand”? Walk away.
-
Check Referring Domains: If it’s 80% garbage tier referring sites or a bunch of redirects powering the DR/DA, the root is tainted.
-
Language Match: Don’t build links on random foreign domains unless you’re targeting that country, or it’s a specifically very strong site and you don’t regularly acquire other geo’s TLDs. Irrelevant geo links can trigger trust issues.
Pro Tip: Use Wayback Archive, Whois.com and NameBio.com to check for previous site history, domain ownership and any auction sales.
6. Editorial Integrity & Link Sell Signals
-
Does the site publish 5+ guest posts a day? Probably a link farm…
-
Do they accept any niche under the sun for $50? Run.
-
Does content read like it’s actually targeting humans, or is it AI slop & images stitched together to sell posts? That’s your answer.
Pro Tip: Good publishers still sell links, but they hide it well on the site or are very limited. If the site screams “pay me for links,” Google’s algo can probably smell it too.
7. Campaign Fit & Velocity
-
Supporting Page Strategy: Build links not just to your money page but to supporting content, then internally link. This stacks authority naturally, protects your money pages from potentially toxic links and allows you to better distribute equity through internals.
-
Anchor Distribution: Save exact match anchors for your very best placements. Spread branded and natural anchors across the rest.
-
Velocity Matching: Don’t drop 200 links in a month if competitors are building 10–20, and you are only publishing 3 blog posts and one new page a month. Match your site and the SERP’s velocity curve.
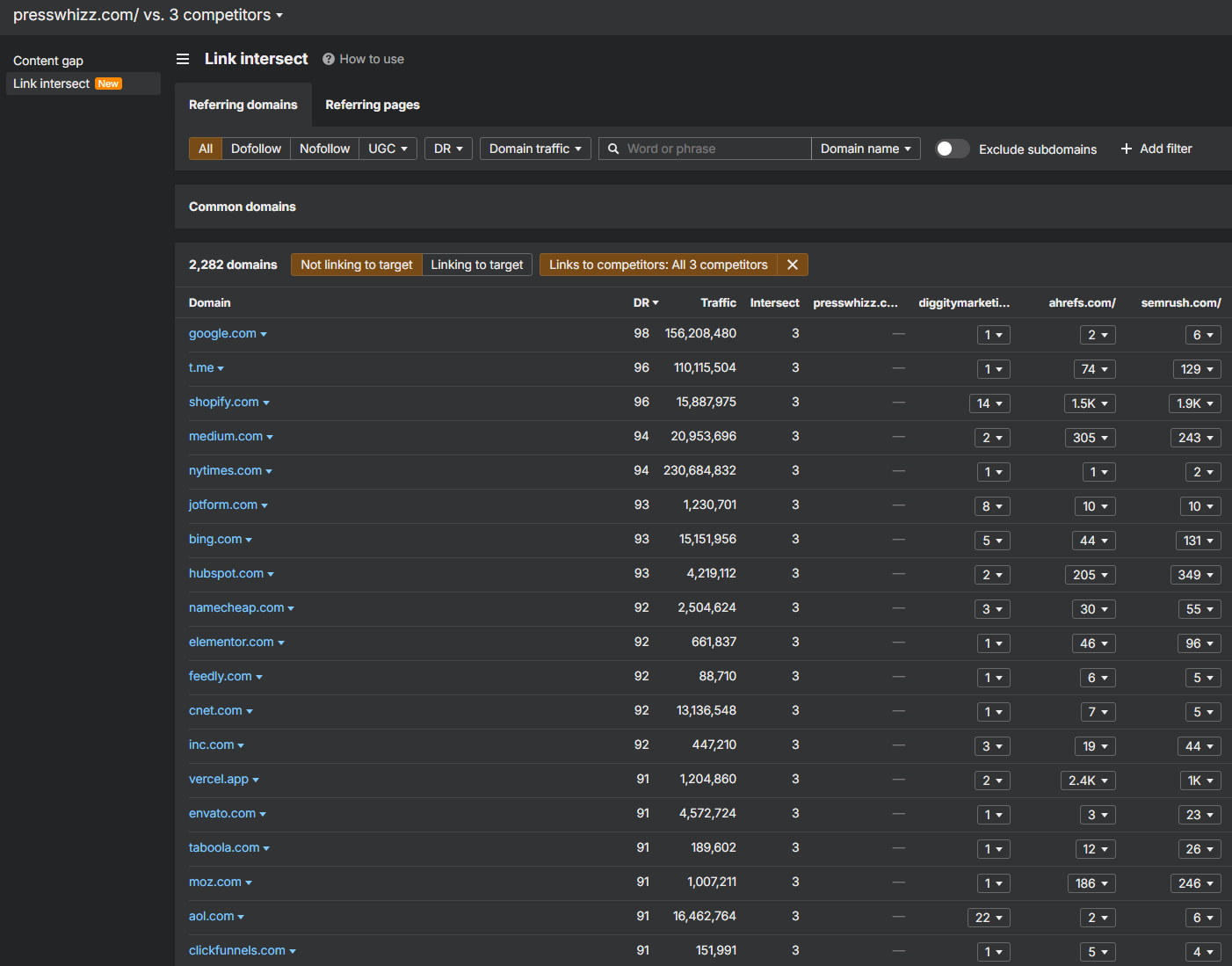
Pro Tip: Always map your backlink campaigns against your top 10-50 competitors. Intersect what they have, then outdo them with smarter placement.
You can use the Ahrefs Competitor Link intersect tool, as an example I put in 3 competitors to see which referring domains they had and we didn’t –
Can You Rank Without Backlinks?
Short answer: yes, for low competition, ultra specific queries.
Long answer: it’ll be slow, brittle, and you’ll cap out fast.
Links are the throttle; without them you’re idling.
When “NO Links” Can Still Win
You can rank without deliberate link building when:
-
Query difficulty is genuinely low. Top 10 pages have ~0–5 RDs/page, weak DR sites, thin content, and no serious brands.
-
Long-tail / local / informational intent. “how to reset [obscure device] 2026”, “best [niche part] torque spec”, “[suburb] [micro-service] after hours”.
-
SERP has no heavy hitters. Few or no big publishers, UGC results, thin forums, or stale content.
Even then, you’ll likely wait longer to get crawled and indexed, especially if you’re not feeding Google signals (see below). No GSC? You just made the crawl lottery harder.
Most People Forget: You’re ALREADY Building Links
Spinning up social and entity profiles is link building if you put your site in the bio. And it matters, especially for new sites.
I already went through entity stacking at the start of the blog post, but just to reaffirm what I mean:
-
Company/brand profiles: LinkedIn Page, X/Twitter, Facebook Page, Instagram (if visual), YouTube (even empty but branded), GitHub (dev/SaaS), Crunchbase, ProductHunt/AngelList (startup), BBB/Chamber (local), citations (Yelp, Foursquare, HotFrog, local directories).
-
Google properties: Business Profile (if local), News/Publisher where relevant, a clean XML sitemap in Google Search Console, site ownership verified, URL Inspection to push priority pages, and a brand-centric About/Contact/Author footprint.
-
NAP (name/address/phone number) consistency everywhere, and Organization/Person schema on-site and in links.
Call it “pillow” or “entity” links, either way, they accelerate crawl, reduce ambiguity, and lift brand trust at the edges
Why Most People Should Still Build Links
Here’s the thing: The answer is no, you cannot rank without backlinks for 90%+ of projects.
If you’re trying to rank for anything even remotely competitive, whether it’s “best lawyer in [city],” “crypto exchange reviews,” or “cheap flights 2026” then you’re not getting anywhere without links.
Even in “new” niches or underserved local markets, the window for easy mode SEO is closing fast.
Google is stuffing SERPs with:
-
Authority publishers (Forbes, NYT, niche media sites)
-
Aggregator brands (Yelp, Tripadvisor, LegalZoom, Healthline clones)
-
AI-content spam at scale that gets cleaned up only when Google shifts the dial again
So what’s left? Links. As always! They’re the lever that tips you above the noise.
But the real question isn’t do you need them, it’s how many links do you need? And subsequently, where do do you need them and pointed at what?
How Many Links Do You Need?
Here’s my 8 step framework for analyzing how many links it requires to rank, planning them out, and even an example case study demonstration.
And if you don’t want to go through all of these advanced steps, then there’s a TL’DR below.
1) Quantify the Gap (Data > Vibes)
- Pull the top 10 for your target keyword(s). For each ranking URL, record:
- Page-level RDs (referring domains)
- Domain DR/DA
- Content depth & last update
- Internal links into the page (approx., from crawlers)
- Set your baseline target per page:
- Low comp:
median RD of top 3(or +20% if you’re a weaker domain) - Medium comp:
top 3 average RD + 30–50%(compensates for brand bias) - High comp/brand-heavy: plan supporting content links + root authority, not just direct links (more below)
- Low comp:
Rule of thumb: if the page-one median has 8–15 RDs, you won’t bypass it with “great content.” Start planning actual link numbers.
2) Prioritize by Revenue, Then Difficulty
Stack-rank your pages by money impact (lead value/AOV/affiliate EPC) × opportunity (how close you are).
- Quick wins: pages sitting positions 5–15 with a gap ≤10 RDs.
- Strategic wins: money pages where brand sites dominate; you’ll need supporting links + root authority.
- Foundation: build the entity/citation/brand links to grease everything else (you already started this above).
3) Decide Where Links Go (Sculpt, Don’t Spray)
You’re not just “buying links to money pages.” You’re wiring authority through your site:
- Root Authority (Homepage / Brand Assets)
- Use digital PR, high-DR profiles/interviews, big publications.
- Purpose: Raise sitewide trust so future pages rank with fewer direct links.
- Money Pages (Direct Fire)
- Use editorial guest posts, high-quality niche edits, relevant news mentions.
- Purpose: Close the page-level RD gap. Save exact/partial anchors for the best placements only.
- Hub / Category Pages
- Earn/buy links to hubs that internally link to money pages.
- Purpose: Create authority nodes that drip-feed equity via internals (safer for aggressive niches).
- Supporting Content (Satellites)
- Build links to informational pages that contextually link into money pages.
- Purpose: Tip tougher SERPs without over-optimizing anchors on the money URL.
4) How Many Links (Ballpark You Can Actually Use)
- Low competition:
- Per money page: 5–15 quality RDs (editorial/niche-relevant) + a few brand/PR to root.
- Usually enough to break into top 3 once on-page & internals are tight.
- Medium competition:
- Per money page: 20–60 quality RDs over 2–4 months.
- Plus 5–15 to 2–3 supporting pieces that point in; 2–5 strong root authority links.
- High competition (brands in SERP):
- Per money page: 60–200+ over 3–9 months.
- You’ll also need consistent root authority (digital PR), links to hubs, and ongoing supporting content links.
Use the SERP gap to set the initial quota, then review weekly for movement. If you’re stuck at #5–#8 after hitting the quota, the bottleneck is usually anchors, internal links, or root authority — not “more of the same.”
5) Anchor Text Plan (Be Precise, Not Paranoid)
Across the whole campaign to a money page:
- Branded / URL / generic: 60–80% (dominant share)
- Partial-match / topical phrases: 15–30%
- Exact-match: 0–10% (save for your highest-quality placements only)
- Image/naked/noanchor from PR/profile/citations naturally fill the rest
If the SERP is sensitive (YMYL / legal / finance), push even heavier brand anchors and rely on contextual relevance of the linking page to carry semantics.
6) Velocity That Won’t Trip Wires
- Match the SERP + your publish cadence. If you publish 3 posts/mo, don’t blast 50 links/mo at one URL.
- New sites: start with entity + pillow links, then ramp to 5–15 quality links/mo across targets.
- Aged domains: you can accelerate, but distribute across money pages + hubs + supports.
Simple governor: for most sites, link growth should lag content growth by ~1–3 weeks. It looks and is more natural.
7) Tiering & Activation (Optional but Potent)
- Tier 2s to your best editorial placements (mix nofollow/dofollow from relevant blogs/UGC).
- Purpose: “Activate” sleepy nofollow news links and amplify great dofollow ones without touching the money page again.
8) Internal Links: The Free Multiplier
- Every time you ship a new link to any page, add 2–5 contextual internals into your target.
- Use descriptive anchors (not EM).
- Keep a hub → spokes structure; update hubs quarterly.
An Example Case Study
- SERP median = 12 RDs per top-3 page; you’re at 2 RDs.
- Plan:
- 10–15 new quality RDs to the money page over 8–16 weeks.
- 4–6 links to 2 supporting guides that interlink to the money page.
- 2–3 brand/PR links to root.
- Anchors: ~70% brand/generic, 20–25% partials, 1–2 exacts (on best pages only).
- Add 6–10 new internal links into the money page (from hubs/related posts).
- Review at week 6: if stuck around #6–#9, raise root authority (PR) or add another 5–10 to the supporting content instead of hammering the money URL again.
What to Track (So You Don’t Fly Blind)
- Positions & impressions (page level) weekly
- Indexation of every placement (and rel attr)
- Referring domains (unique only; ignore sitewide noise)
- Anchor mix (campaign view)
- Internal link count into target pages
- Time-to-crawl after each batch (if slow, build more trusted-source links)
TL;DR
- Count the SERP gap → set a real quota.
- Split links across root / money / hubs / supports.
- Keep anchors boringly safe except for your very best spots.
- Match velocity to the SERP + your publishing frequency.
- Use internals and occasional tiering to multiply every paid link.
Do this, and you won’t ask “do links still work?”, you’ll ask “how fast can we responsibly scale this without tripping classifiers?”
Final Thoughts & The Future of Links
As AI systems ingest, summarize, and arbitrate truth at scale, they still need attribution and consensus.
Whether it’s a link or an unlinked brand mention tied to your entity, machines will keep asking the same question: who else says this is true? The web’s reputation layer doesn’t evaporate because the interface changed; it just gets scored differently.
Mentions, citations, and co-occurrence around your brand are becoming soft links that reinforce the hard ones.
That trust is modeled through graphs: knowledge, link, and entity graphs, all converging on the same outcome: Sites with recognized reputation rank faster, get crawled deeper, and recover quicker.
If you’re building for the next 24 months, build authority systems, not one off placements, unless you’re doing churn and burn or black hat.
Practically, that means shifting a chunk of your effort into citation worthy assets (original data, proprietary tools, defensible guides etc), digital PR that earns both links and mentions, and brand distribution across high trust nodes (Think news, industry orgs, conferences, or even academic/gov references where possible).
Treat backlinks like a portfolio: Mix root authority PR, niche editorial context, supporting page links, and a steady cadence of entity/pillow signals that make the whole profile look alive. Then maintain it, as links decay, pages get noindexed, anchors get edited; winners monitor and refresh.
As Google and big tech utilizing AI lean harder into consensus and reliability, the operators who consistently manufacture credible citations, clickable or not, will own the compounding.
Build assets people must reference, seed them where machines listen, and wire the equity through your site with intent. The interface will keep changing; the economics of trust won’t.


